Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis
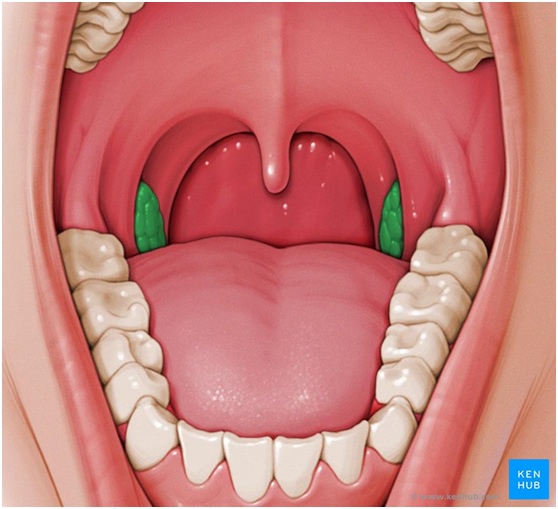
What is tonsillitis?
Tonsils apart from adenoids are the human body's first line of defense as part of the immune system. Tonsils are two lumps, similar to lymph nodes situated at the back of the throat.
They filter bacteria and viruses that enter the body through the mouth or nose, but they themselves can sometimes become infected. Tonsillitis is an infection of the tonsils caused by viruses and bacteria. When tonsillitis occurs the tonsils get inflamed and swell up causing nasal obstruction and/or breathing, swallowing, and sleep problems. Tonsillitis usually is contagious for about 7-10 days.
What are the causes of tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils due to infection by viruses and bacteria. It is a very common childhood condition and can occur at any age. Tonsils produce white blood cells which combat viruses and bacteria that enter the body through the mouth. But if the immune system is weak, especially in children, overworked, and elderly people then the tonsils become vulnerable during the attack by the viruses and bacteria and get infected.
The most common cause of tonsillitis is viruses. The viruses cause infections such as the common cold and flu, and there is the EBV virus (part of the herpes family which spreads through bodily fluids, most commonly through kissing) that causes mononucleosis or mono also known as the kissing disease.
Here are some of the common viruses that cause tonsillitis:
• Adenoviruses
• Influenza virus
• Epstein-Barr virus
• Parainfluenza viruses
• Enteroviruses
• Herpes simplex virus
• The most common bacterium that causes tonsillitis is the one that causes strep throat especially in children, called Streptococcus pyogenes.